1. Silk Cocoons
2. De-gummed Silk Cocoons
3. Carded cocoon strippings or floss
4. Throwster’s waste
5. Silk carrier rods
Silk with sericin (or gummed silk) can be used in silk paper making or it can be de-gummed and used in more adventurous types of spinning.
1. Silk Cocoons
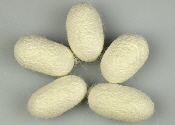
What can you do with whole silk cocoons? As well as being useful for educational purposes, cocoons can be used in many crafts. You can degum them and then stretch them on a frame to make silk hankies, or spin the silk cocoons into a yarn full of character. Alternatively, you can cut them into pieces and use them to make silk paper. You can even try to reel your own silk yarn.
|
|
|
mulberry silk cocoons
|
|

|
|
Degummed silk cocoons
|
|

|
|
Carded cocoon strippings
|
|

|
|
Throwster’s waste
|
|

|
|
Silk carrier rods
|
|
You can also obtain cut silk cocoons, which can be dyed and made into jewellery or used in other crafts. Buy silk cocoons here.
2. De-gummed silk cocoons
Degummed silk cocoons are soft fluffy balls made by removing the sericin from the cocoons. They more affordable than silk tops and easier than tops to handle in the dye pot. They are fun to spin and add to felt making. Buy degummed silk cocoons here.
3. Carded cocoon strippings or floss
When the silkworm is ready to start spinning a cocoon, it makes a scaffolding which is used as the framework for spinning the cocoon. The silk used for the scaffolding forms a halo of floss around the cocoon. This silk is a little bit thicker than the silk used to spin the cocoon and it is also made of shorter fibres. Commercial cocoons no longer have this ‘halo’ as silk farmers remove the thin loose layer of floss before sending the cocoons to the market.
Until recently this time consuming operation was done by hand. Simple deflossing devices are being developed which speed up the process from 20 kg of cocoons per hour when carried out by hand to 50 to 100 kg per hour by machine.
The floss is not wasted; it is carded and sold as carded cocoon strippings. This type of silk contains sericin and it is great for making textured silk paper. Buy carded cocoons strippings here.
4. Throwster’s waste
A throwster is someone who twists together raw silk filaments that have been reeled from a cocoon, turning the filaments into thread. The waste is the silk that could not be used in this process. It includes short pieces and long tangled threads.
Throwsters waste, or silk waste, is available for sale in two types, either gummed or degummed. Gummed silk waste still has sericin (the cocoon glue) which makes it feel dry and brittle, and somewhat wiry. In this state it can be used to make silk paper with the sericin acting as the adhesive that holds the paper together. Buy gummed silk waste here.
Degummed silk waste has had the sericin removed and it is soft and lustrous. It contains a mixture of short and long pieces of silk, as well as curly and tangled strands, giving it a great deal of texture. Degummed silk waste takes dyes well. The long strands of silk can then be mixed with wool and used to add lustre to felt. If you want to use it for spinning or blending, you will need to cut the threads into shorter pieces, otherwise they will become tangled in your carder. Buy degummed silk waste here.
5. Silk carrier rods
Silk carrier rods are formed during silk reeling, which is the process of unwinding silk from cocoons to make yarn. The filament that is being unwound passes over a rod called the ‘carrier rod’. During the reeling process filaments get wrapped at high speed around the carrier rod, to which some stick.
As they still have sericin (the natural gum that was holding the filaments together in the shape of a cocoon), they get attached to neighbouring filaments. When the build up of filament becomes too thick, the silk tube is cut with a knife and removed from the rod. The result is a slit tube 13 to 15 cm long made of criss-crossed filaments of silk. They are great for creating texture in your art work. They are easy to use in silk paper making and make an unusual addition to felt making. Buy silk carrier rods here.
Back to Mulberry Silk Fibre
1. Mulberry silk tops & bricks
2. Mulberry silk noils
3. Mulberry silk hankies & Mawata silk caps
Top of page
|

